Ultrasound - Breast
- What is Ultrasound Imaging of the Breast?
- What are some common uses of the procedure?
- How should I prepare?
- What does the equipment look like?
- How does the procedure work?
- How is the procedure performed?
- What will I experience during and after the procedure?
- Who interprets the results and how do I get them?
- What are the benefits vs. risks?
- What are the limitations of Ultrasound Imaging of the Breast?
What is Ultrasound Imaging of the Breast?
Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also called ultrasound scanning or sonography, involves the use of a small transducer (probe) and ultrasound gel placed directly on the skin. High-frequency sound waves are transmitted from the probe through the gel into the body. The transducer collects the sounds that bounce back and a computer then uses those sound waves to create an image. Ultrasound examinations do not use ionizing radiation (as used in x-rays), thus there is no radiation exposure to the patient. Because ultrasound images are captured in real-time, they can show the structure and movement of the body's internal organs, as well as blood flowing through blood vessels.
Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions.
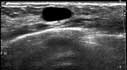
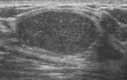
Ultrasound imaging of the breast produces a picture of the internal structures of the breast.
Doppler ultrasound is a special ultrasound technique that evaluates blood flow through a blood vessel, including the body's major arteries and veins in the abdomen, arms, legs, neck and head (in infants and children).
During a breast ultrasound examination the sonographer or physician performing the test may use Doppler techniques to evaluate blood flow or lack of flow in any breast mass. In some cases this may provide additional information as to the cause of the mass.
What are some common uses of the procedure?
- Determining the Nature of a Breast Abnormality
The primary use of breast ultrasound today is to help diagnose breast abnormalities detected by a physician during a physical exam (such as a lump or bloody or spontaneous clear nipple discharge) and to characterize potential abnormalities seen on mammography or breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Ultrasound imaging can help to determine if an abnormality is solid (which may be a non-cancerous lump of tissue or a cancerous tumor) or fluid-filled (such as a benign cyst) or both cystic and solid. Ultrasound can also help show additional features of the abnormal area.
Doppler ultrasound is used to assess blood supply in breast lesions.
- Supplemental Breast Cancer Screening
Mammography is the only screening tool for breast cancer that is known to reduce deaths due to breast cancer through early detection. Even so, mammograms do not detect all breast cancers. Some breast lesions and abnormalities are not visible or are difficult to interpret on mammograms. In breasts that are dense, meaning there is a lot of ducts, glands, fibrous tissue and less fat, many cancers can be hard to see on mammography.
Many studies have shown that ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help supplement mammography by detecting breast cancers that may not be visible with mammography. MRI is more sensitive than ultrasound in depicting breast cancer, but MRI may not be available to all women. If screening MRI is performed, then screening ultrasound is not needed, though ultrasound may be used to characterize and biopsy abnormalities seen on MRI. When ultrasound is used for screening, many more abnormalities that may require biopsy are seen than are seen with mammography or MRI. These abnormalities usually are not cancer (false positives), and this limits its usefulness.
Ultrasound can be offered as a screening tool for women who:
- are at high risk for breast cancer and unable to undergo an MRI examination.
- are pregnant or should not be exposed to x-rays (which is necessary for a mammogram).
- Ultrasound-guided Breast Biopsy
When an ultrasound examination reveals a suspicious breast abnormality, a physician may choose to perform an ultrasound-guided biopsy. Because ultrasound provides real-time images, it is often used to guide biopsy procedures. An ultrasound exam will usually need to be performed before the biopsy in order to plan the procedure and to determine if this method of biopsy can be used.
For more information on this procedure, please refer to the Ultrasound-guided Breast Biopsy page (www.RadiologyInfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=breastbius).
How should I prepare?
You will be asked to undress from the waist up and to wear a gown during the procedure.
What does the equipment look like?
Ultrasound scanners consist of a console containing a computer and electronics, a video display screen and a transducer that is used to do the scanning. The transducer is a small hand-held device that resembles a microphone, attached to the scanner by a cord. The transducer sends out inaudible high frequency sound waves into the body and then listens for the returning echoes from the tissues in the body. The principles are similar to sonar used by boats and submarines.
The ultrasound image is immediately visible on a video display screen that looks like a computer or television monitor. The image is created based on the amplitude (loudness), frequency (pitch) and time it takes for the ultrasound signal to return from the area of the patient being examined to the transducer (the device used to examine the patient), as well as the type of body structure and composition of body tissue through which the sound travels. A small amount of gel is put on the skin to allow the sound waves to travel back and forth from the transducer.
How does the procedure work?
Ultrasound imaging is based on the same principles involved in the sonar used by bats, ships and fishermen. When a sound wave strikes an object, it bounces back, or echoes. By measuring these echo waves, it is possible to determine how far away the object is as well as the object's size, shape and consistency (whether the object is solid or filled with fluid).
In medicine, ultrasound is used to detect changes in appearance, size or contour of organs, tissues, and vessels or detect abnormal masses, such as tumors.
In an ultrasound examination, a transducer both sends the sound waves and receives the echoing waves. When the transducer is pressed against the skin, it directs small pulses of inaudible, high-frequency sound waves into the body. As the sound waves bounce off internal organs, fluids and tissues, the sensitive microphone in the transducer records tiny changes in the sound's pitch and direction. These signature waves are instantly measured and displayed by a computer, which in turn creates a real-time picture on the monitor. One or more frames of the moving pictures are typically captured as still images. Small loops of the moving “real time” images may also be saved.
Doppler ultrasound, a special application of ultrasound, measures the direction and speed of blood cells as they move through vessels. The movement of blood cells causes a change in pitch of the reflected sound waves (called the Doppler effect). A computer collects and processes the sounds and creates graphs or color pictures that represent the flow of blood through the blood vessels.
How is the procedure performed?
You will lie on your back on the examining table and may be asked to raise your arm above your head.
After you are positioned on the examination table, the radiologist or sonographer will apply a warm water-based gel to the area of the body being studied. The gel will help the transducer make secure contact with the body and eliminate air pockets between the transducer and the skin that can block the sound waves from passing into your body. The transducer is placed on the body and moved back and forth over the area of interest until the desired images are captured.
There is usually no discomfort from pressure as the transducer is pressed against the area being examined. However, if scanning is performed over an area of tenderness, you may feel pressure or minor pain from the transducer.
Doppler sonography is performed using the same transducer.
Once the imaging is complete, the clear ultrasound gel will be wiped off your skin. Any portions that are not wiped off will dry to a powder. The ultrasound gel does not stain or discolor clothing.
What will I experience during and after the procedure?
Ultrasound examinations are painless and easily tolerated by most patients.
Breast ultrasound is usually completed within 30 minutes.
If a Doppler ultrasound study is performed, you may actually hear pulse-like sounds that change in pitch as the blood flow is monitored and measured.
You may be asked to change positions during the exam.
When the examination is complete, you may be asked to dress and wait while the ultrasound images are reviewed.
After an ultrasound examination, you should be able to resume your normal activities immediately.
Who interprets the results and how do I get them?
A radiologist, a physician specifically trained to supervise and interpret radiology examinations, will analyze the images and send a signed report to your primary care physician, or to the physician or other healthcare provider who requested the exam, and he/she will share the results with you. In some cases the radiologist may discuss results with you at the conclusion of your examination.
Follow-up examinations may be necessary, and your doctor will explain the exact reason why another exam is requested. Sometimes a follow-up exam is done because a suspicious or questionable finding needs clarification with additional views or a special imaging technique. A follow-up examination may also be necessary so that any change in a known abnormality can be monitored over time. Follow-up examinations are sometimes the best way to see if treatment is working or if an abnormality is stable over time.
What are the benefits vs. risks?
Benefits
- Most ultrasound scanning is noninvasive (no needles or injections).
- Occasionally, an ultrasound exam may be temporarily uncomfortable, but it is almost never painful.
- Ultrasound is widely available, easy-to-use and less expensive than other imaging methods.
- Ultrasound imaging is extremely safe and does not use any ionizing radiation.
- Ultrasound scanning gives a clear picture of soft tissues that do not show up well on x-ray images.
- Ultrasound provides real-time imaging, making it a good tool for guiding minimally invasive procedures such as needle biopsies and fluid aspiration.
- Ultrasound imaging can help detect lesions in women with dense breasts.
- Ultrasound may help detect and classify a breast lesion that cannot be interpreted adequately through mammography alone.
- Using ultrasound, physicians are able to determine that many areas of clinical concern are due to normal tissue (such as fat lobules) or benign cysts. For most women 30 years of age and older, a mammogram will be used together with ultrasound. For women under age 30, ultrasound alone is often sufficient to determine whether an area of concern needs a biopsy or not.
Risks
- For standard diagnostic ultrasound, there are no known harmful effects on humans.
- Interpretation of a breast ultrasound examination may lead to additional procedures such as follow-up ultrasound and/or aspiration or biopsy. Many of the areas thought to be of concern only on ultrasound turn out to be non-cancerous.
What are the limitations of Ultrasound Imaging of the Breast?
- Ultrasound is one of the tools used in breast imaging, but it does not replace annual mammography and careful clinical breast examination.
- Many cancers are not visible on ultrasound.
- Biopsy may be recommended to determine if a suspicious abnormality is cancer or not.
- Most suspicious findings on ultrasound that require biopsy are not cancers.
- Many calcifications seen on mammography cannot be seen on ultrasound. Some early breast cancers only show up as calcifications on mammography. MRI findings that are due to cancer are not always seen with ultrasound.
- Many facilities do not offer ultrasound screening, and the procedure may not be covered by some insurance plans.
- It is important to choose a facility with expertise in breast ultrasound, preferably one where the radiologists specialize in breast imaging. Ultrasound depends on the abnormality being recognized at the time of the scan as it is a "real-time" examination. This requires experience and good equipment. One measure of a facility's expertise in breast ultrasound can be found in its ACR accreditation status. Check the facilities in your area by searching the ACR-accredited facilities database.
Additional Information and Resources
RadiologyInfo
Breast Cancer
(www.RadiologyInfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=breastcancer)
RTAnswers.org
Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer
(www.rtanswers.com/treatmentinformation/cancertypes/breast/index.aspx)
Locate an ACR-accredited provider: To locate a medical imaging or radiation oncology provider in your community, you can search the ACR-accredited facilities database.
This website does not provide costs for exams. The costs for specific medical imaging tests and treatments vary widely across geographic regions. Many—but not all—imaging procedures are covered by insurance. Discuss the fees associated with your medical imaging procedure with your doctor and/or the medical facility staff to get a better understanding of the portions covered by insurance and the possible charges that you will incur.
Web page review process: This Web page is reviewed regularly by a physician with expertise in the medical area presented and is further reviewed by committees from the American College of Radiology (ACR) and the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), comprising physicians with expertise in several radiologic areas.
Outside links: For the convenience of our users, RadiologyInfo.org provides links to relevant websites. RadiologyInfo.org, ACR and RSNA are not responsible for the content contained on the web pages found at these links.
Images: Images are shown for illustrative purposes. Do not attempt to draw conclusions or make diagnoses by comparing these images to other medical images, particularly your own. Only qualified physicians should interpret images; the radiologist is the physician expert trained in medical imaging.
This page was reviewed on July 15, 2013