Glossary of Terms
Enter
a term in the text box and press Find.
For a list of terms, select a letter or enter starting letter(s). |
|
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
M
N
O
P
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
[All]
|
|
|
- abdominal aorta
- Part of the aorta, the largest artery in the body; it supplies oxygenated blood to the abdominal and pelvic organs and legs.
Click image to view larger
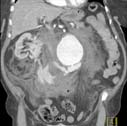
- abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)
- Sometimes called triple A.
A ballooning out of a segment of artery caused by disease or weakness in the vessel wall (called an aneurysm) that occurs in the portion of the aorta that runs through the abdomen. For more information, see the Abdominal aortic aneurysm page.
- ablation
- See radiofrequency ablation.
- abscess
- A localized infection consisting of pus surrounded by inflamed tissue.
- absence seizure
- See petit mal seizure.
- absorption
- (ab-sorp-shun)
- In radiology, the uptake of energy from radiation by the tissue or medium through which it passes.
- In radiation or medical physics, the number of disintegrations per second of a radionuclide.
- acetaminophen
- A drug that reduces pain and fever but not inflammation. A member of the family of drugs called analgesics, it is found in many over-the-counter medications, such as Tylenol®.
- acute
- Referring to the rapid onset of a disease or condition.
- adenoma
- A type of potentially precancerous polyp, an abnormal growth that protrudes from the inner wall of the colon. The majority of colorectal cancers develop from adenomas.
- adjuvant therapy or treatment
- Treatment designed to be contributory or complementary to primary therapy. See also definitive.
- afterloaded implant
- A brachytherapy treatment in which a remote-controlled machine pushes radioactive material through a delivery device to the site of a tumor.
- allergy
- A hypersensitive reaction to common, often harmless substances, most of which are found in the environment.
- allograft
- Tissue graft from a separate donor.
- Allopurinol
- A drug that lowers an elevated level of uric acid in the blood caused by some cancer treatments.
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin (A1AT)
- A protein that protects the lung. A1AT deficiency puts a person at risk of developing emphysema or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (A1AD)
- A genetic disorder caused by low levels of a protein called alpha-1 antitrypsin.
- alveoli
- Tiny air sacs located at the end of the respiratory tract in the lungs that allow inhaled oxygen to enter the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to leave the bloodstream with exhalation.
- amniocentesis
- (am-nE-O-sen-tE-sis)
- The suction of fluid from the amniotic sac through the use of a needle inserted through the abdomen.
- amnion
- (am-nE-on)
- See amniotic sac.
- amniotic sac
- (am-nE-o-tik)
- Membrane filled with fluid within the abdomen that holds the embryo/fetus.
- analgesic
- A drug that relieves pain.
- anemia
- A condition in which too few red blood cells are in the bloodstream, resulting in insufficient oxygen to tissues and organs. For additional information see the Anemia page.
- anesthesia
- Drugs used to induce loss of sensation for the patient in preparation for operative procedures.
- anesthesiologist
- A physician specializing in the controlled loss of sensation through anesthesia.
- anesthetics
- Drugs used to induce loss of sensation for the patient in preparation for operative procedures.
Click image to view larger
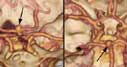
- aneurysm
- (an-yur-izm)
- A ballooning out of a segment of blood vessel caused by disease or weakness in the vessel wall. It may lead to rupture and serious or fatal bleeding.
- angina
- (an-jye-nah)
- Cramp-like pain that comes and goes, and is made worse by physical effort. It is a sign that the tissue or organ supplied by a narrowed artery is not getting enough blood or oxygen. For more information see the Angina Pectoris page.
- angiocardiography
- (an-jE-O-kar-dE-O-gra-fE)
- X-ray imaging of the heart, coronary arteries and/or great vessels made visible by injection of a dye directly into the vessel via a catheter. In other instances, CT or MRI can be used to create three-dimensional pictures of blood vessels.
- angiogenesis
- Formation of new blood vessels.
- angiogenesis inhibitors
- Drugs that interfere with the growth of blood vessels in the tumor, thus starving the tumor of the nutrients and oxygen it needs to grow. Also called angiostatic therapy.
- angiogram
- In a conventional angiogram, a dye is injected into the bloodstream and x-rays are taken to visualize the blood vessels. In other instances, CT or MRI can be used to create three-dimensional pictures of blood vessels.
- angiographic
- (an-jE-O-graf-ik)
- Relating to or utilizing angiography.
Click image to view larger

- angiography
- (an-jE-og-ra-fE)
- Radiography of vessels after the injection of a radiopaque contrast material. Unlike angioplasty, which is an invasive procedure, angiography breaks the skin only for the insertion of a needle for administering a radiopaque catheter and positioning under fluoroscopic control. This technique is used to image arteries in the brain, heart, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, aorta, neck, chest, limbs and pulmonary circuit.
- angioplasty
- (an-jE-O-plas-tE)
- Reconstitution or reopening of a blood vessel; may involve balloon dilation, mechanical stripping of the inside of the blood vessel, forceful injection of a elastic filamentous protein, or placement of a stent. For details see the Angioplasty and Vascular Stenting page.
- angiostatic therapy
- See angiogenesis inhibitors.
- annulus
- The outer layer of intervertebral discs, sponge-like cushions between the vertebrae, or bones, of the spine.
- anonymization
- The process of removing all indentifiers or codes that directly or indirectly link a sample or data to a specific identifiable person.
- anterior fibromuscular stroma
- The anterior surface of the prostate.
- antibiotics
- A class of medications used to treat bacterial infections by killing or inhibiting the growth of bacteria.
- antibodies
- Substances that neutralize body toxins and bacteria.
- anticoagulant therapy
- (an-tI-cO-ag-U-lant ther-a-pE)
- The use of anticoagulant drugs to reduce or prevent intravascular or intracardiac clotting.
- anticonvulsant
- A drug used to prevent or reduce the severity of seizures associated with epilepsy or other seizure disorders.
- antiplatelet drug
- A medication that interferes with the normal function of blood platelets and thereby reduces the tendency for blood to clot; commonly called a blood thinner.
- aorta
- (A-Or-ta)
- The large artery leaving the heart that distributes blood to the entire body through branches.
- aortic aneurysm
- A ballooning-out of a segment of artery caused by disease or weakness in the vessel wall (called an aneurysm) that occurs in the aorta.
- appendiceal lumen
- Inside of the appendix where mucus, created by the appendix, travels and empties into the large intestines.
Click image to view larger

- appendicitis
- An inflammation of the appendix, usually caused by a blockage of the opening of the "pouch" and a subsequent infection. For more information see the appendicitis page.
- appendicolith
- A stone, calcification or calcific deposit in the appendix.
- appendix
- A wormlike "pouch" several inches long located near the beginning of the large intestine, in the lower right portion of the abdomen. At this time, the role the appendix plays in the human body is not known.
- arachnoid membrane
- A thin membrane enclosing the brain and spinal cord. The subarachnoid space lies between the arachnoid membrane and the spinal cord.
- argon gas
- A colorless, odorless gas found in the air and used in its liquefied state in cryosurgery to freeze and destroy diseased tissue, including cancer cells.
- arrhythmia
- An abnormal rhythm of the heart.
- arteriosclerosis
- (ar-tEr-E-O-skler-O-sis)
- Hardening of the arteries; types generally recognized are: atherosclerosis, Mönckeberg's arteriosclerosis, and arteriolosclerosis.
- arteriovenous fistula
- An abnormal connection between an artery and a vein. This can be surgically created for hemodialysis (see dialysis arteriovenous fistula) but can also be caused by trauma. These fistulas can commonly be treated by interventional radiologists.
- arteriovenous malformation (AVM)
- An abnormal communication between an artery and vein that may be present at birth or may result from injury or infection. Blood may flow directly from the artery to the vein, bypassing the small vessels where oxygen and tissue nutrients are exchanged. These unusual malformations are often found in the brain and spinal cord, but may occur anywhere in the body.
- A tangle of dilated blood vessels that disrupts normal blood flow in the brain.
- artery
- Vessels that carry blood away from the heart.
- arthritis
- (arth-rI-tis)
- Inflammation of a joint or a state characterized by inflammation of joints. For more information see the Arthritis page.
- arthrography
- An imaging study of a joint that uses a contrast material and either magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or a special form of x-ray imaging called fluoroscopy.
- artifact
- In radiology, something artificial that appears on a medical image but is not a part of the living tissue being examined. The image distortion could be due to an obstruction, such as a surgical metal clip, or to a problem with the imaging equipment.
- asbestos
- A group of minerals with long, thin fibers that occur naturally in the environment; asbestos was once used in housing and commercial materials. Asbestos inhalation can cause a variety of health problems (e.g., asbestosis, pleural effusion, mesothelioma or lung cancer).
- ascites
- An accumulation of fluid in the abdomen that may be caused by cirrhosis (chronic liver disease), cancer, heart failure, kidney failure, tuberculosis and pancreatic disease.
- aspirin
- A member of the family of drugs called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAID) that reduces pain, fever, inflammation, and blood clotting.
- asthma
- A condition of the lungs characterized by a constriction of the airways and secretion of mucus that interferes with normal air movement causing wheezing.
- asymptomatic
- Having no signs or symptoms.
- atherectomy
- A minimally invasive treatment for blocked arteries that uses a catheter with a sharp blade or laser on the end to remove plaque from a blood vessel.
Click image to view larger
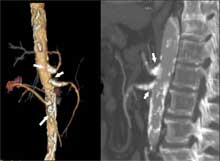
- atherosclerosis
- (ath-er-O-skler-O-sis)
- Arteriosclerosis characterized by irregularly distributed lipid deposits, or plaque, in large and medium-sized arteries; such deposits provoke fibrosis and calcification (hardening of the tissues).
- atrophy
- (at-rO-fE)
- A wasting of tissues, organs, or the entire body.
- attenuation
- (u-ten-yU-A-shun)
- Loss of energy of a beam of radiant energy due to absorption, scattering, beam divergence, and other causes as the beam propagates through a medium.
- audit
- An information system log that keeps a record of all user activity by user identification.
- aura
- A visual disturbance, such as flashing lights, wavy lines, blurry vision or blind spots, that sometimes occurs prior to the onset of a migraine headache.
- authentication
- Verifying the identity of a person/user to a computer system or assuring that a computer program is a trusted one.
- authorization
- Access controls that restrict access to a system to only authorized users; access control assigns right and privileges of users to resources via single sign-on databases; auto logoff to prevent someone other than the valid user from continuing a session; physical access control for critical computers to prevent console-based malicious attacks, power interruptions or other threats to security of the systems.
- autoimmune disease
- Any disorder that causes the immune system to attack the body’s own tissues.
- automated needle
- An automated needle is a spring-loaded device that cuts and retrieves a small tissue specimen in its collecting chamber.
- axillary lymph node dissection
- Surgical exploration and removal of lymph nodes from the armpit area, as a part of breast cancer surgery. Some or all of these lymph nodes are examined under a microscope by a pathologist (a physician specializing in the examination of cells and tissues) to see if cancer cells are present.
- axillary lymph nodes
- (ax-il-ArE limf nOdz)
- Numerous nodes around the axillary (below the shoulder joint) veins which receive the lymphatic drainage from the upper limb, scapular region and pectoral region (including mammary gland); they drain into the subclavian trunk.
- axons
- See nerve fibers.
|
|